- Home
- -Blog
5 levels of agile planning

- 27 FEB 2024
- Admin
5 levels of agile planning
Agile planning is not just a methodology; it's a mindset that empowers teams to deliver value to their customers efficiently and effectively. Unlike traditional project management approaches, which often rely on rigid, linear plans, Agile embraces change, encouraging continuous feedback and iterative development. This approach allows teams to remain flexible, adjusting their strategies as project requirements evolve.
Agile planning unfolds across multiple levels, each with a distinct focus and timeframe. This multi-tiered approach ensures that planning is both strategic and tactical, encompassing long-term goals while also addressing immediate tasks and deliverables. The concept of planning at different levels—ranging from the overarching vision of the project down to daily tasks and activities—helps teams navigate complex projects by breaking them down into manageable segments.
According to the 14th Annual State of Agile Report, a significant percentage of organizations report that adopting Agile practices has led to enhanced ability to manage changing priorities, increased project visibility, improved business/IT alignment, and faster time to market. These benefits highlight how Agile planning not only streamlines project management but also aligns closely with business objectives, ensuring that teams are working on what's most valuable to their customers.
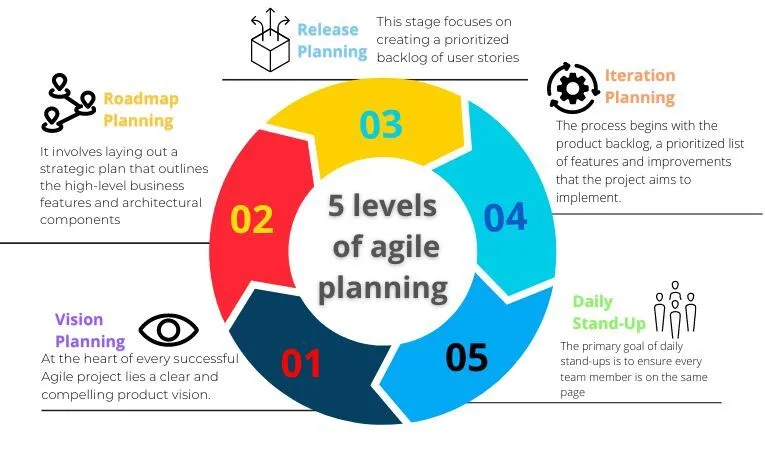
Vision Planning
At the heart of every successful Agile project lies a clear and compelling product vision. This vision serves as a north star, guiding all team efforts and ensuring that everyone is moving in the same direction.
Establishing a clear product vision is crucial because it aligns the team's work with the overall goals of the project. It ensures that every feature developed, every decision made, is aimed at achieving this overarching objective.
But how do we ensure that this vision is not just clear but also resonates with our target audience? This is where the concept of defining customer roles and creating personas comes into play.
Personas are fictional characters that represent your ideal customers. By understanding who you are building the product for, you can tailor your vision to meet their specific needs, challenges, and aspirations.
Creating personas involves researching and outlining the characteristics, behaviors, and motivations of your target audience. This process helps in crafting a vision statement that is precise and customer-centric.
Example 1: if your product is a financial app designed for young professionals, your vision statement should reflect how your app addresses their unique financial planning needs, preferences for digital solutions, and lifestyle goals.
A well-defined product vision, supported by detailed customer personas, ensures that your project is not just a collection of features but a solution that solves real problems for real people.
It provides a framework for decision-making, helping teams prioritize features and initiatives that contribute most effectively to the vision. Moreover, it keeps the team motivated and focused, as they have a clear understanding of the impact their work has on the end users.
Roadmap Planning
Roadmap planning is a critical step in translating your Agile project's vision into actionable steps. It involves laying out a strategic plan that outlines the high-level business features and architectural components necessary to achieve the product vision.
A roadmap is essentially a bridge between the lofty goals set in your vision statement and the day-to-day tasks that your team will undertake. It serves as a guide, showing how the project will evolve over time, detailing milestones, and setting expectations for stakeholders.
Creating a roadmap that aligns with the product vision means breaking down the vision into major features and improvements that need to be made to bring that vision to life.
Each item on the roadmap should contribute directly to the overarching goals of the project, ensuring that all efforts are focused and coherent. This process requires a deep understanding of the product vision, the market, the users, and the technological landscape.
A well-crafted roadmap offers a strategic plan for achieving long-term goals. It helps teams prioritize work, making it easier to decide what to work on first and what can wait. By laying out the planned features and updates over time, a roadmap makes it clear what the team is aiming to achieve in the next quarter, the next year, or even further into the future. This long-term perspective is essential for maintaining alignment between the team's activities and the product's ultimate objectives.
Insights from AgileConnection, Kanban Zone, and Jile highlight the importance of flexibility in roadmaps. Agile projects are dynamic, with changes and new insights constantly arising. Therefore, while a roadmap provides a plan, it's also important that it's adaptable. As new information becomes available or priorities shift, the roadmap can be updated to reflect these changes without losing sight of the product vision.
In summary, roadmap planning is an essential exercise in strategic thinking, breaking down the product vision into achievable steps and setting the direction for the project's development. It not only ensures that all team efforts are aligned with the long-term goals but also provides a flexible framework that can adapt to the inevitable changes that occur in any Agile project.To facilitate this process, businesses can work with experienced strategic planning consultants who can help refine the plan and align it with broader organizational goals.
Release Planning
Release planning in Agile project management is a critical phase where teams outline the specific features, enhancements, and fixes that will be developed and released in the upcoming cycle.
This stage focuses on creating a prioritized backlog of user stories, which are concise descriptions of features from the perspective of the end user. These user stories serve as the building blocks for planning the work that will be tackled in the next release.
The process of release planning involves collaboration among team members to identify which user stories are most crucial to the project's success. The goal is to strike an optimal balance between delivering high-value features that address user needs and ensuring the technical infrastructure is robust and scalable.
This balance is pivotal because focusing too much on one aspect can lead to challenges—prioritizing only user-facing features might neglect the necessary backend improvements, while focusing solely on technical infrastructure could delay the delivery of features that users need and want.
AgileConnection and Kanban Zone both emphasize the importance of this balance. They advocate for a methodology where both the product's functionality and its underlying architecture are considered in tandem. This dual focus ensures that the product evolves in a way that satisfies users and stakeholders, while also maintaining a strong, reliable, and scalable technical foundation.
An effective release plan also involves setting realistic timelines and expectations. By prioritizing user stories, teams can allocate their resources efficiently, focusing first on what adds the most value to the product. This prioritization is often guided by the product roadmap and the vision planning stages, ensuring that each release brings the product closer to its ultimate goals.
Moreover, the dynamic nature of Agile projects requires that release plans be flexible. Changes in market conditions, user feedback, or technical discoveries should be incorporated into the planning process. This adaptability is a strength of Agile methodologies, allowing teams to pivot as needed to ensure the product remains relevant and competitive.
In summary, release planning is a delicate balancing act that requires careful consideration of what features and improvements are most important, how they align with the overall product vision, and how they can be executed within the project's technical constraints. By focusing on creating a prioritized backlog of user stories and maintaining a balance between feature development and technical infrastructure, teams can ensure that their Agile projects are successful and deliver value to users and stakeholders.
Iteration Planning
Iteration planning is a key component of Agile project management, focusing on breaking down features into deliverable user stories for each iteration. This process is essential for translating the broader goals of the project into specific, actionable tasks that can be completed within a short, predetermined period—usually two to four weeks.
The process begins with the product backlog, a prioritized list of features and improvements that the project aims to implement. During iteration planning, the team selects items from this backlog that they can commit to delivering by the end of the iteration. Each selected item, or feature, is then broken down into smaller, more manageable pieces called user stories. These stories are crafted to be specific enough to guide development while remaining flexible to changes that may arise during the iteration.
User stories typically follow a simple format that outlines who the user is, what they need, and why they need it. This structure helps ensure that the development work remains focused on delivering value to the user.
The technical team plays a crucial role in this process, collaborating closely with business stakeholders to ensure that the project scope is both ambitious and achievable. This collaboration is vital for adapting and refining the project scope based on feedback and new insights that emerge during development. AgileConnection and Kanban Zone both emphasize the importance of this ongoing dialogue between the technical team and business stakeholders. It ensures that the project remains aligned with business objectives while also being technically sound and feasible.
The iterative nature of this planning process allows teams to make adjustments as they learn more about the user's needs and the technical challenges that arise. This flexibility is a hallmark of Agile methodologies, enabling teams to pivot quickly in response to new information or changes in the project environment.
In summary, iteration planning is about turning big ideas into small, achievable goals, ensuring that each step of the project brings tangible value. Through close collaboration between the technical team and business stakeholders, and by focusing on deliverable user stories, teams can navigate the complexities of development with agility and precision, ensuring that the final product meets both business and user needs.
Daily Stand-Up
Daily stand-up meetings are a cornerstone of Agile methodology, designed to enhance team communication and swiftly address any impediments that may hinder project progress. These brief, typically 15-minute gatherings serve a dual purpose: they keep everyone informed of the project's current status and foster a collaborative environment where issues can be identified and resolved quickly.
The primary goal of daily stand-ups is to ensure every team member is on the same page, understanding what others are working on and where they might need help. By sharing updates on what was accomplished since the last meeting, what's on the agenda for today, and any obstacles in the way, the team can effectively coordinate their efforts and maintain momentum. This consistent check-in helps in identifying potential delays early, allowing the team to devise solutions before they escalate into more significant issues.
Moreover, daily stand-ups contribute significantly to maintaining alignment with the iteration's objectives. They remind the team of the bigger picture, ensuring that day-to-day activities are closely aligned with the iteration goals. This alignment is crucial for Agile teams, where flexibility and rapid response to change are valued. By regularly revisiting and reinforcing the iteration's objectives, the team can stay focused on delivering value in line with the project's overall goals.
AgileConnection and Jile, along with other Agile resources, highlight how daily stand-ups are not merely status updates but strategic tools that empower teams. They provide a platform for open communication, foster a sense of accountability, and promote quick decision-making, all of which are vital for the dynamic environment of Agile projects.
In essence, daily stand-ups are a vital practice within Agile methodologies, ensuring teams communicate effectively, remain aligned with their objectives, and address challenges proactively. This practice is a key driver in sustaining project momentum and achieving successful outcomes in an Agile setting.
Implementing Agile Planning in Your Projects
Implementing Agile planning into your projects is a transformative step that brings about increased flexibility, enhanced collaboration, and a greater capacity to adapt to change. Here are some practical tips to effectively apply the five levels of Agile planning in project management:
- Embrace the Vision: Start with a strong, clear vision that guides all aspects of your project. This vision should be concise and align with the needs and goals of your customers. Ensure every team member understands and is committed to this vision, as it will inform the direction of your project from start to finish.
- Develop a Roadmap: Your roadmap is your strategic plan. It should outline the key milestones and features that need to be developed to achieve your vision. Remember, a roadmap is a living document. It needs to be flexible enough to accommodate changes in strategy or priorities.
- Focus on Release Planning: Release planning translates your strategic goals into actionable objectives. Prioritize your backlog of user stories based on value to the customer and technical feasibility. Balance high-impact features with the necessity of maintaining a robust technical infrastructure.
- Iterate with Purpose: Iteration planning breaks down your features into deliverable chunks of work. Use this time to ensure that what you're planning to deliver aligns with your overall goals. Encourage collaboration between the technical team and business stakeholders to refine and adapt the project scope as needed.
- Leverage Daily Stand-Ups: Daily stand-ups are crucial for maintaining momentum and alignment. They keep the team focused on the day's objectives and quickly address any impediments. Foster an environment where issues can be openly discuss+3ed and solutions are collaboratively sought.
Flexibility and Collaboration: The iterative nature of Agile planning requires a mindset of project collaboration, and openness to change.. Agile is not just a set of practices but a way of thinking that values adaptability over strict adherence to a predefined plan.
Encourage Team Collaboration: Effective Agile planning relies on the active participation of all team members. Encourage open communication and collaboration across all levels of planning. Utilize tools and practices that enhance teamwork, such as shared digital workspaces, pair programming, and cross-functional teams.
Continuous Improvement: Agile planning is an ongoing process. After each iteration, take the time to reflect on what worked, what didn't, and how processes can be improved. This continuous cycle of planning, executing, and evaluating fosters a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
Customer-Centric Approach: Always keep the customer at the center of your planning. Agile planning is about delivering value to the customer through a product that meets their needs and exceeds their expectations. Regularly gather customer feedback and use it to inform your planning and development processes.
By following these tips and maintaining a focus on flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement, you can successfully implement Agile planning in your projects. This approach will not only enhance your project management practices but also lead to higher-quality outcomes and greater customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Adopting Agile planning practices is a strategic move toward achieving better project outcomes and boosting team performance. By integrating the five levels of Agile planning into your processes, you invite flexibility, collaboration, and a customer-focused approach into your project management. This shift not only aligns your team with the dynamic demands of today's market but also sets the stage for continuous improvement and innovation. Embrace Agile planning, and propel your projects and team toward greater success.



